The Carpentries: How We Operate
Overview
Teaching: 30 min
Exercises: 45 minQuestions
How is The Carpentries organized and run?
What is the difference between SWC, DC, and LC workshops?
Objectives
Get connected with the Carpentry community.
Describe where you can go to get information on running a workshop.
In becoming a certified Carpentries instructor, you are also becoming part of a community of like-minded volunteers. This section provides some background on The Carpentries projects and information about how to get involved.
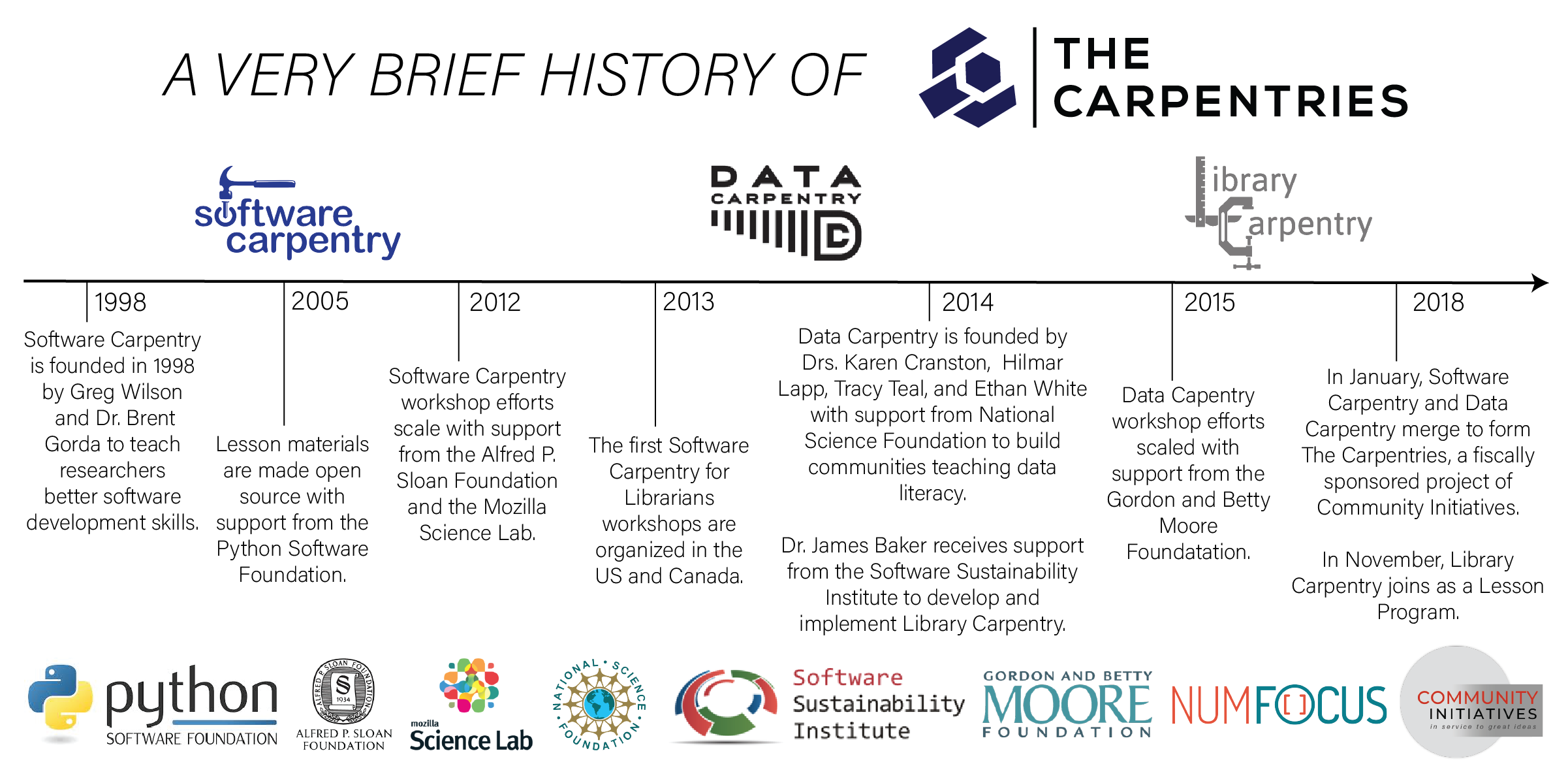
A Brief History
Software Carpentry was founded in 1998 with the mission of teaching lab skills for research computing. Data Carpentry was founded in 2014 with the mission of building communities teaching universal data literacy. Also in 2014, Library Carpentry was founded with the mission of teaching data skills to people working in library- and information-related roles.
On January 1, 2018, Software Carpentry and Data Carpentry merged their projects to form a new project called The Carpentries under the fiscal sponsorship of Community Initiatives. Within this new organization structure, Software Carpentry and Data Carpentry retain their individual identities as Lesson Programs of the Carpentries. On November 1, 2018, The Carpentries Executive Council approved Library Carpentry as the third official Lesson Program of the Carpentries.
The Carpentries project comprises communities of Instructors, Trainers, Maintainers, helpers, and supporters from Software Carpentry), Data Carpentry and Library Carpentry who share a mission to teach foundational computational and data science skills.
You can learn more about the history and goals of each Lesson Program by reading “Software Carpentry: Lessons Learned”, “Data Carpentry: Workshops to Increase Data Literacy for Researchers” and “Library Carpentry: software skills training for library professionals””.
Similarities and Differences between The Carpentries Lesson Programs
All lesson programs under The Carpentries share the same value of promoting efficient, shareable, and reproducible research practices. Their aligned missions are accomplished by running accessible, inclusive training workshops; teaching openly available, high-quality, domain-tailored lessons; and fostering an active, inclusive, diverse instructor community that promotes and models reproducible research as a community norm.
Similarities between Software, Data and Library Carpentry workshops include:
- a focus on technical skills.
- two-day format taught by volunteer instructors.
- a focus on filling gaps in current training for learners.
The major different between Software, Data and Library Carpentry workshops is their content and intended audience.
Software Carpentry workshops are:
- intended for people who need to program more effectively to solve their computational challenges,
- not domain-specific, and
- modular—each Software Carpentry lesson is standalone.
Data Carpentry workshops:
- are aimed at pure novices,
- are domain-specific,
- focus on best practices surrounding data, and
- present a full curriculum centered around a single data set.
Library Carpentry workshops:
- are aimed at people in library- and information-related roles.
- focus on best practices in data structure, and
- are modular—each Library Carpentry lesson is standalone.
The Carpentry Community
The Carpentries works to help institutions and individuals spread skills for data analysis, computational thinking, and research software development through building local and global communities of practice. Our community depends on individuals like you who are passionate about expanding these communities of practice through inclusive and evidence-based instructional practices, and can contribute your perspective and expertise to continually refine our instructional materials and practices. A full description of the breadth and diversity of community member roles, an overview of the Carpentries’ various social media channels, a calendar of future community events, and descriptions of mailing lists used by the community can be found here on the Carpentries website and also on the getting connected page.
Participating in the Carpentries – What’s Your Role?
If you are at an in-person training, your instructor will hand out paper copies of a worksheet. If you are at an online training, you can get a digital copy here.
Take a moment to review member community roles on the Carpentries’ community website. Working on your own, match up the roles with the descriptions. When you are done, think about the question at the bottom of the worksheet about what roles you might play, and enter your thoughts in the etherpad.
Solution
Instructors: C Mentors: E Trainers: D Lesson developers: J Curriculum advisors: B Lesson maintainers: F Lesson Infrastructure Team: I Assessment Team: K Champions: L Infrastructure Team: H Workshop Administrators: A Code of Conduct Committee: G
This exercise should take about 10 minutes.
Get Connected
Take a couple of minutes to sign up for the Carpentry discussion channels you want to stay involved with.
How a Workshop Works
There are two types of Carpentry workshops: self-organized and centrally-organized. For a centrally-organized workshop, Carpentry staff takes care of organization and administration such as finding instructors and handling workshop registration. For a self-organized workshop, all of these details are handled by the instructors or organization hosting the event.
If you would like to host a Software Carpentry workshop at your institution, information can be found on the request a Software Carpentry workshop page.
If you would like to host a Data Carpentry workshop at your institution, visit Data Carpentry centrally-organized workshops and Data Carpentry self-organized workshops.
Policies related to instructor training and workshops for both Software Carpentry and Data Carpentry can be found in the policies repository. Please be sure to read through the instructor no-show policy before signing up for your first workshop.
Materials
All of Software Carpentry, Data Carpentry, and Library Carpentry lessons materials are freely available under a permissive open license. You may use them whenever and however you want, provided you cite the original source.
Using the Names and Logos
The names “Software Carpentry”, “Data Carpentry” and “Library Carpentry” and their respective logos are all trademarked. You may only call a workshop a Software Carpentry, Data Carpentry, or Library Carpentry workshop if:
- it covers the core topics,
- at least one instructor is certified,
- you run our standardized pre- and post-workshop assessments and ensure everyone participates, and
- you send us summary information about attendees (at a minimum, the number of people who attended).
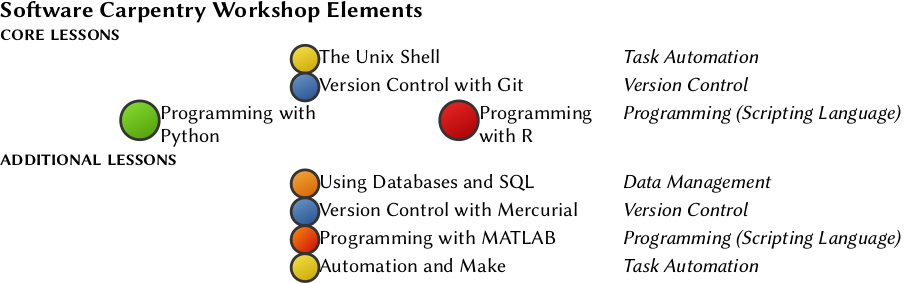
What is the Core Curriculum?
A Software Carpentry workshop must include lessons on version control (e.g. Git), the UNIX shell, and a programming language (e.g. R or Python).
A Data Carpentry workshop must include a Data Carpentry lesson on data organization and three other modules in the same domain from the Data Carpentry curriculum. Published curricula include the Ecology, Genomics, Social Science and Geospatial workshop materials. Additionally, Astronomy, Digital humanities, Economics and Image analysis curriculum are under development.
A Library Carpentry workshop must include three to four of the core lessons, which include an introduction to data, the UNIX shell, OpenRefine, and Git. Library Carpentry maintains an “extended” set of lessons that can be taught in addition to the core curriculum. These lessons are taught infrequently and/or are under development and include: SQL, webscraping, Python, and an introduction to data for archivists.
Within these guidelines, there is flexibility in which episodes of the lesson you cover, which exercises you use, and whether you include optional materials (e.g. callouts) and optional episodes.
Who Can Teach What
As of March 2017, a trained instructor can teach curricula for either Software Carpentry or Data Carpentry and are no longer required to certify separately for each: see the description of the instructor checkout procedure for details.
Setting Up
In order to communicate with learners, and to help us keep track of who’s taught what and where, each workshop’s instructors create a one-page website with information about their workshop. Once that has been created, the host or lead instructor sends its URL to the workshop coordinator, who adds it to our records. The workshop will show up on our websites shortly thereafter.
Practice With SWC or DC Infrastructure
Go to the workshop template repository and follow the directions to create a workshop website using your local location and today’s date. Put the link for your workshop website into the Etherpad.
This exercise should take about 25 minutes.
Question and Answer
What questions do you have about running and teaching at a workshop? Talk with a partner and enter your questions into the Etherpad. At this time we will also return to discuss questions remaining from the beginning of the day.
Leave about 10 minutes for this discussion.
A Culture of Contribution
In the same way that we hope to promote a culture of openness, sharing, and reproducibility in science and research through training researchers with the tools they need, the Carpentry organizations themselves aim to be open, collaborative, and based on best practices. We want to draw together the collective expertise of our teaching community to create collaborative lessons, share other materials, and improve the lessons via “bug fixes” as we go along.
Lesson Incubation
Maybe this instructor training has inspired you to go home and write your own fantastic lesson! If you’d like to model it after the Software and Data Carpentry lesson format, you can find a template and instructions in the Carpentries lesson example repository.
Many Ways to Contribute
We recognize that the medium of GitHub may be restrictive to those who wish to contribute to our lessons. We are always searching for ways to make the process more friendly to all, whether that be contribution training, or alternative routes to contribution. If you have any ideas how we might make contribution more contributor-friendly, please let us know.
Being part of a friendly, open discussion, is of equal or greater importance to the community than submitting the perfect lesson change. The checkout process to become a certified instructor will be one way to start connecting to the community and find which area will allow you to contribute best.
Key Points
Carpentry materials are all openly licensed, but Software and Data Carpentry names and logos are trademarked.
Carpentry workshops must cover core concepts, have at least one certified instructor, use our pre- and post-workshop surveys and report attendance information.